Top 10 Strongest Currencies in the World in 2025 (Highest Valued in INR)
In 2025, the global economy continues to evolve, and the value of currencies fluctuates based on a wide range of factors including economic performance, inflation, political stability, and trade balances. Among the currencies that have stood out for their strength are those that offer high exchange rates against the Indian Rupee (INR), making them the most valued in the international market. This article takes a closer look at the top 10 strongest currencies in the world in 2025, as valued in INR.
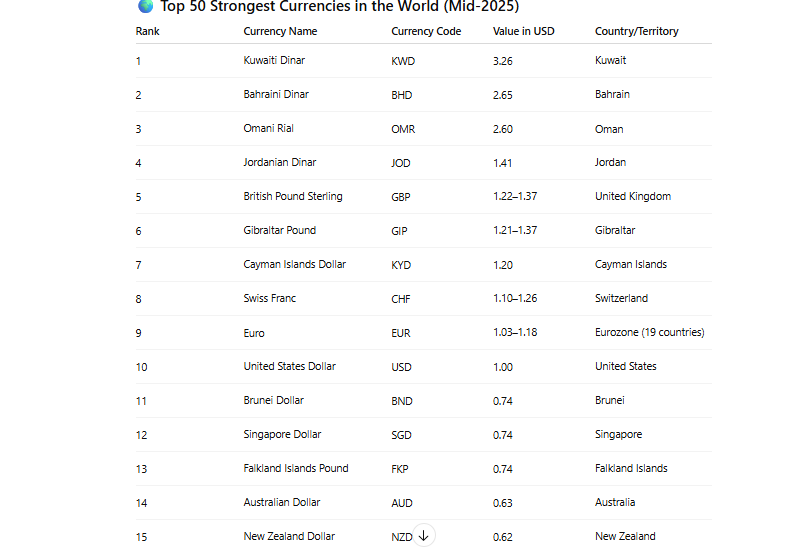
1. Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD)
The Kuwaiti Dinar has consistently held the top spot as the world’s strongest currency, and 2025 is no exception. With a single Kuwaiti Dinar being valued at a significant amount of INR, it reflects Kuwait’s prosperous oil-driven economy and stable government policies.
- Current Exchange Rate (KWD to INR): 1 KWD ≈ ₹266.5
2. Bahraini Dinar (BHD)
Bahrain’s currency, the Bahraini Dinar, remains one of the strongest currencies globally. The Kingdom of Bahrain has a robust financial sector, and its currency is highly valued due to the nation’s strong economic fundamentals, particularly in oil and banking.
- Current Exchange Rate (BHD to INR): 1 BHD ≈ ₹235.3
3. Omani Rial (OMR)
The Omani Rial is known for its high value against the Indian Rupee. Oman’s rich oil reserves and fiscal prudence contribute to the strength of its currency. Oman’s stable government and relatively low inflation rate further support the Rial’s strength in 2025.
- Current Exchange Rate (OMR to INR): 1 OMR ≈ ₹233.4
4. Jordanian Dinar (JOD)
Despite its smaller economy, Jordan’s currency, the Jordanian Dinar, has consistently remained one of the highest-valued currencies in the world. Jordan’s stable political environment and the country’s reliance on foreign aid and remittances have helped maintain the Dinar’s strong value.
- Current Exchange Rate (JOD to INR): 1 JOD ≈ ₹158.9
5. British Pound Sterling (GBP)
The British Pound is one of the oldest and most historically powerful currencies. The UK economy, despite the challenges posed by Brexit, continues to maintain a robust position in global trade and finance. The Pound’s value against the INR in 2025 remains strong due to the nation’s diversified economy and the strength of its financial sector.
- Current Exchange Rate (GBP to INR): 1 GBP ≈ ₹108.5
6. Euro (EUR)
The Euro, shared by 20 countries in the Eurozone, is one of the most widely used and powerful currencies in the world. The Euro’s value against the Indian Rupee remains high due to the European Union’s combined economic might, despite challenges in the post-pandemic era.
- Current Exchange Rate (EUR to INR): 1 EUR ≈ ₹92.2
7. Swiss Franc (CHF)
Switzerland has long been known for its stable economy, financial sector, and political neutrality. The Swiss Franc is traditionally viewed as a “safe haven” currency, and its value remains strong in 2025, bolstered by Switzerland’s highly developed economy and low inflation rate.
- Current Exchange Rate (CHF to INR): 1 CHF ≈ ₹91.1
8. US Dollar (USD)
The US Dollar, while not the strongest currency in 2025, remains one of the most influential currencies in the world. It is widely used in international trade, finance, and as a reserve currency by central banks around the globe. The value of the Dollar remains significant against the INR due to the size and stability of the US economy.
- Current Exchange Rate (USD to INR): 1 USD ≈ ₹82.6
9. Canadian Dollar (CAD)
The Canadian Dollar holds its ground as one of the stronger currencies in 2025, bolstered by Canada’s abundant natural resources, solid financial sector, and strong trade relations, especially with the United States. While it isn’t as strong as the US Dollar or Euro, it has maintained a stable exchange rate.
- Current Exchange Rate (CAD to INR): 1 CAD ≈ ₹61.3
10. Singapore Dollar (SGD)
Singapore, a global financial hub and trade center, has a strong and highly valued currency in 2025. The Singapore Dollar is backed by the nation’s robust economy, excellent infrastructure, and political stability. With a strong export sector, particularly in electronics and biotechnology, the SGD maintains its value against the INR.
- Current Exchange Rate (SGD to INR): 1 SGD ≈ ₹60.8
Factors Influencing Currency Strength
Several factors contribute to the strength of these currencies, including:
- Economic Stability: Countries with strong economies, low inflation rates, and steady growth tend to have stronger currencies.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks that maintain tight monetary policies and keep inflation low can help ensure the strength of a nation’s currency.
- Political Stability: Countries that have stable governments and low political risk usually see their currencies perform better.
- Commodity Exports: Many of the strongest currencies, such as the Kuwaiti Dinar and Omani Rial, benefit from high oil prices due to their large oil exports.
- Trade Surpluses: Countries that export more than they import generally see their currencies strengthen over time due to increased demand for their currency in international trade.
Conclusion
As we look toward 2025, the strongest currencies in the world are those that represent countries with high levels of economic development, political stability, and low inflation. The Kuwaiti Dinar, Bahraini Dinar, and Omani Rial lead the list due to their high value relative to the Indian Rupee, followed by other strong currencies such as the British Pound, Euro, and Swiss Franc. As global economic dynamics continue to shift, these currencies will likely remain powerful in the years to come.
Check: SBI Clerk Notification 2025
FAQs
1. What are the strongest currencies in the world?
The strongest currencies in the world are typically those with high exchange rates against major global currencies like the US Dollar (USD) or the Euro (EUR). As of recent years, currencies such as the Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD), Bahraini Dinar (BHD), Omani Rial (OMR), and Jordanian Dinar (JOD) are often considered some of the strongest.
2. What makes a currency “strong”?
A strong currency is typically characterized by its high value relative to other currencies. Factors contributing to a currency’s strength include:
-
Economic stability: Countries with stable economies tend to have stronger currencies.
-
Low inflation: Currencies from countries with low inflation rates usually hold more value.
-
Demand for the currency: A high demand for a country’s goods, services, and financial assets increases the demand for its currency, strengthening it.
-
Interest rates: Higher interest rates attract foreign capital, which can strengthen the currency.
3. Which currency is the most expensive in the world?
The Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD) is currently the most expensive currency in the world when exchanged against the US Dollar (USD).
4. What is the relationship between a strong currency and a country’s economy?
While a strong currency is often a sign of a healthy and stable economy, it can have mixed effects. For instance:
-
Positive effects: It lowers the cost of imports and can help reduce inflation. It can also make a country’s assets attractive to foreign investors.
-
Negative effects: A very strong currency may hurt export competitiveness because it makes the country’s goods and services more expensive for foreign buyers.
5. Do strong currencies always indicate a strong economy?
Not necessarily. While many strong currencies come from economically stable countries, there are exceptions. Some countries may have artificially strong currencies due to government policies, such as pegs to other currencies or economic measures that keep the currency value high.
6. Why do some small countries have strong currencies?
Small countries like Bahrain and Oman have strong currencies due to several reasons, including a high level of wealth, a strong financial sector, and a reliance on the export of valuable natural resources such as oil.
7. Are all the strongest currencies from developed countries?
Not all of them. Some of the strongest currencies come from countries that are not considered large economies or traditional financial powers. For example, Kuwait, Qatar, and Bahrain have strong currencies despite not having large populations or being global financial centers.
8. What does the exchange rate of a strong currency mean for tourists?
For tourists traveling to countries with strong currencies, the cost of living and expenses may be higher. This is because the exchange rate makes foreign goods and services more expensive. For instance, traveling to countries like Switzerland (CHF) or Norway (NOK) might be costlier for someone using a weaker currency.
9. How do strong currencies affect international trade?
A strong currency can make a country’s exports less competitive due to higher prices for foreign buyers. However, it can make imports cheaper, benefiting companies and consumers in the domestic market who rely on foreign goods.
10. Can the value of a currency change over time?
Yes, the value of a currency can fluctuate due to factors like:
-
Changes in government policies
-
Economic conditions (recession, growth, inflation)
-
Shifts in global market trends
-
Changes in international trade balances
11. Is it better to invest in countries with strong currencies?
It depends on the context. A strong currency might indicate a stable economy, making the country attractive for investment. However, if the currency is too strong, it could harm the competitiveness of domestic industries. Investors should consider factors like economic growth potential, political stability, and the investment climate.
12. How does a country maintain a strong currency?
Countries maintain strong currencies through:
-
Sound monetary policies: Keeping inflation low and stable.
-
Strong fiscal discipline: Ensuring government debt is manageable.
-
Export-driven economies: Generating demand for the country’s currency through exports.
-
Attractive interest rates: Encouraging foreign investment, which boosts demand for the currency.
13. How can currency strength affect tourism?
Tourism can be affected because travelers from countries with weaker currencies will find it more expensive to visit countries with stronger currencies. On the flip side, travelers from countries with strong currencies can afford more when they travel to weaker currency nations.
14. How do central banks manage currency value?
Central banks manage currency value by using monetary tools like adjusting interest rates, controlling inflation, and engaging in foreign exchange market interventions. For example, if a currency is too weak, a central bank may raise interest rates to attract foreign investment, thereby strengthening the currency.
15. Which currency is expected to become stronger in the future?
It’s difficult to predict with certainty. However, currencies from countries with growing economies, low inflation, and increasing international demand, such as the Singapore Dollar (SGD) or the Australian Dollar (AUD), may become stronger over time.
16. Do exchange rates reflect a country’s entire economic performance?
Exchange rates reflect various factors such as the strength of the economy, interest rates, inflation, political stability, and trade balances. However, they don’t give a complete picture of a country’s economic health because other internal factors like GDP growth or unemployment might not be fully captured.
17. How often do currency rankings change?
Currency rankings can change frequently depending on shifts in economic conditions, trade imbalances, inflation rates, and geopolitical events. While the strongest currencies like the Kuwaiti Dinar and Bahraini Dinar remain at the top for long periods, fluctuations in global markets can cause changes in the rankings.